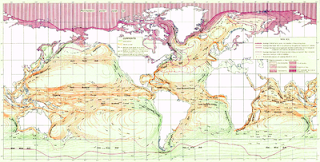
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon the water, such as the Earth's rotation, wind, temperature, salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. Depth contours, shoreline configurations and interaction with other currents influence a current's direction and strength.
Ocean currents can flow for thousands of kilometers, and together they create the great flow of the global conveyor belt which plays a dominant part in determining the climate of many of the Earth’s regions. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate than any other region at the same latitude. Another example is the Hawaiian Islands, where the climate is cooler (sub-tropical) than the tropical latitudes in which they are located, because of the effect of the California Current.


No comments:
Post a Comment